If tutorials available on this website are helpful for you, please whitelist this website in your ad blocker😭 or Donate to help us ❤️ pay for the web hosting to keep the website running.
Operator एक symbol होते हैं , जो process / operation represent करते हैं करते हैं , या हम कह सकते हैं की Operators को कोई process / या operation को perform करने के लिए use करते हैं।
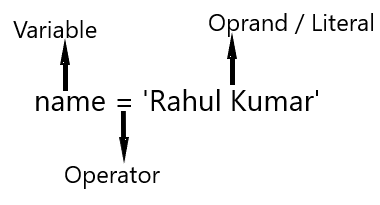
For Example -
x = 10
y = 20
print(x+y)ऊपर दिए गए example में आप देखा सकते हैं कि + (plus sign) Operator define की गयी दो values को add रहा है।
इसी तरह से Python हमें different - different Operators provide कराती है different - different action perform करने के लिए। Python में normally use होने वाले Operators कुछ इस प्रकार हैं -
Note : बाकी languages like PHP , Java , JavaScript की तरह Python increment / decrement operators को support नहीं करता है।
Arithmetic Operators simple calculation में use होने wale Operators होते हैं जैसे Addition , Subtraction etc.
| Operator | Name | Example | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| + | Addition | x+y | ( + ) plus operator uses to add two or more numbers / values |
| - | Subtraction | x-y | ( - ) minus operator uses to substract one numbers / values from another numbers / values or finds the difference |
| / | Division | x / y | quotient of x and y with decimal point. |
| // | Flour Division | x // y | quotient of x and y without decimal point |
| * | multiplication | x * y | product of x and y |
| % | Modulus | x % y | remainder of operands |
| ** | Exponentiation | x ** y | x raised to the power y |
x = 7
y = 3
print("Addition : ", x+y)
print("Subtraction : ", x-y)
print("Division : ", x/y)
print("Floor Division : ", x//y)
print("Multiplication : ", x*y)
print("Modulus : ", x%y)
print("Exponentiation : ", x**y)C:\Users\Rahulkumar\Desktop\python>python arithmetic_op.py Addition : 10 Subtraction : 4 Division : 2.3333333333333335 Floor Division : 2 Multiplication : 21 Modulus : 1 Exponentiation : 343
Assignment Operator को ( = ) से represent करते हैं , जो कि value को किसी variable में assign करने के लिए use किया जाता है। हालाँकि इसे Arithmetic Operators के साथ भी use करते हैं।
| Operator | Name | Example | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| = | Assign | x = y | value of y assigned tox |
| += | Addition then Assign | x += y | First Add and then assign it to x. (It treats like x = x+y) |
| -= | Subtract then Assign | x -= y | get the difference and assign it to x. (It treats like x = x-y) |
| /= | Divide then assign quotient with decimal point, | x /= y | quotient of x and y then assign it to x .( It treats like x = x/y ) |
| // = | Divide then assign quotient without decimal | x //= y | It is same as x = x//y |
| * = | Multiplication then assign the product | x *= y | product of x and y then assign it to x.( It treats like x = x*y ) |
| % = | Divide then assign remainder | x %= y | remainder of operands then assign it to x.( It treats like x = x+%y ) |
x ,y = 7, 3
x += y
print(x)
x,y = 7, 3
x -= y
print(x)
x,y = 7, 3
x /= y
print(x)
x,y = 7, 3
x //= y
print(x)
x,y = 7, 3
x *= y
print(x)C:\Users\Rahulkumar\Desktop\python>python assignment_op.py 10 4 2.3333333333333335 2 21
Comparison Operators दी हुई दो values को compare करके Boolean value True / False return करते हैं. Python में Comparison Operators को कुछ इस तरह से use कर सकते हैं।
| Operator | Name | Example | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| == | Equal | x = = y | checks if x is equal to y. |
| != | Not equal | x != y | checks if x is not equal to y. |
| < | Less than | x < y | checks if x is less than y. |
| > | Greater than | x > y | checks if x is greater than y. |
| <= | Less than or equal | x <= y | checks either x is less than or equal to y. |
| >= | Greater than or equal | x >= y | checks either x is greater than or equal to y |
Logical Operators , एक या एक से अधिक expression के according Boolean value return करते हैं।
| Operator | Name | Example | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| and | And | x and y | Returns True if Both operands (x and y) are true; |
| or | Or | x or y | Returns True if eitherx or y is true; |
| not | not | not(x) | returns True if either x not true; |
जैसा कि name से ही पता चलता है कि किसी variable की identity check हो रही है , for - example : एक variable int type का है या नहीं इसके लिए हम is / is not का use कर सकते हैं।
a = 10
b = '10'
print(type(a) is float)
print(type(a) is int)
print(type(b) is int)
print(type(b) is not int)C:\Users\Rahulkumar\Desktop\python>python identity_op.py False True False True
membership operators का use किसी single element की किसी sequence (like : list , set , dictionary) में existency check करने के लिए use किया जाता है , जैसे हमें ये check करना हो कि किसी list में कोई particular element है या नहीं।
l = [12,45,567,67]
s = {23,45,67,677}
t = (32,4,54656,67)
print(12 in l)
print(120 not in l)
print(23 in s)
print(120 in s)
print(23 in t)
print(32 in t)C:\Users\Rahulkumar\Desktop\python>python membership_op.py True True True False False True
example में तीन variables (list , set और tuple) लिए गएँ हैं इनमे simply check किया है कि कोई particular element उनमे exist करता है या नहीं।
अगर आप list , set और tuple etc के बारे में नहीं जानते तो कोई बात नहीं आगे आप इन्ही के बारे में अच्छे से पढ़ेंगे।
I Hope, अब आप Python में use होने वाले operators के बारे में अच्छे से समझ गए होंगे।

Hi ! I'm Rahul Kumar Rajput founder of learnhindituts.com. I'm a software developer having more than 4 years of experience. I love to talk about programming as well as writing technical tutorials and blogs that can help to others. I'm here to help you navigate the coding cosmos and turn your ideas into reality, keep coding, keep learning :)
Get connected with me. :) LinkedIn Twitter Instagram Facebook